Platelet-rich plasma as a bridge between precision and regenerative medicine
For decades, medical treatments were largely based on the diagnosis of diseases or injuries, rather than on the unique characteristics of each patient or the specific nature of their condition. However, recent advances in genetics, epigenetics and molecular biology have transformed the understanding of how diseases develop and progress. This shift has led to the concept of “precision medicine”, which tailors medical treatments to individuals based on their unique molecular and genetic profiles [1]. This approach has had a significant impact, especially in the field of cancer therapy, and is now being applied and studied in various areas of medicine, from neurodegenerative diseases to genetic, cardiovascular and metabolic disorders [2-5].
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy - a cornerstone in regenerative medicine - is a key strategy for treating musculoskeletal injuries. Its flexibility and targeted protocols enable specific applications. As such, PRP is a promising step towards bridging the gap between regenerative and precision medicine, positioning it as a potentially suitable approach for personalised medicine [6, 7].
PRP: a brief overview of production and potential
PRP is a volume of plasma, usually autologous, that has a platelet concentration above baseline, defined as at least 1 x 106/pL according to the original definitions. It can be obtained through a single or - more frequently - double centrifugation. Briefly, the double centrifugation process consists of the collection of a volume of anticoagulated blood, followed by a consecutive first separation of the majority of the red blood cells from the plasma - which contains platelets, white blood cells and clotting factors - and then a second spin separates the platelets and plasma from the other cells and from the so-called platelet-poor plasma (PPP). Currently, there are no standard protocols for PRP production, due to the presence of many variables among the different techniques to obtain it - e.g., the number of centrifugations, the rotational velocity, centrifugation time chosen and the anticoagulant used - so its composition can vary according to the devices and protocols used in the process [8-10]. This implies that PRP, although it has shown positive results in many fields, cannot often be used as a first-line treatment in daily clinical practice but can be considered for experimental treatments.
Because of its origin, PRP is enriched with many growth factors - especially platelet growth factors - cytokines and cells - such as white blood cells - that can be present in different percentages according to the different PRP formulations. These elements are fundamental in guaranteeing the regenerative, lenitive and immunomodulatory effects of PRP and play a crucial role in promoting cell proliferation, angiogenesis and wound healing (Table 1) [11, 12].
Table 1
List of main growth factors improving tissue healing present in platelet-rich plasma products
| Growth factors | Effects |
|---|---|
| PDGF | |
| VEGF | |
| TGF (α-β) | |
| (a-b) FGF | |
| EGF | |
| IGF-1 | |
| CTGF | |
| IL-8 |
[i] Adapted from Everts [14]
PDGF - platelet-derived growth factor, VEGF - vascular endothelial growth factor, TGF - transforming growth factor, FGF - fibroblast growth factor, EGF - epidermal growth factor, IGF-1 - insulin-like growth factor-1, CTGF - connective tissue growth factor, IL-8 - interleukin-8
PRP growth factors enact their functions primarily via ligand binding to associated extracellular cell receptors, which activate intracellular signalling. This leads to multiple phosphorylation and activation steps of protein kinases until gene transcription occurs in the nucleus, promoting the expression of genes related to tissue healing. Although some authors have pointed out that some PRP components - such as certain pro-inflammatory cytokines or reactive oxygen species released by leukocytes - could have negative effects, this theme is still debated without clear evidence [13].
The variable characteristics of PRP make the realisation of tailored products quite difficult, and its actual composition cannot be confidently predicted in advance. Additionally, the effects of the molecules composing PRP are pleiotropic, and their action should not be evaluated singularly. Moreover, their in vitro or known endogenous effects should not be considered as the only possible results, because PRP components are exogenous and are not related to an internal stimulus. For instance, transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) is a factor whose production is involved in fibrosis, often altering tissue structures. However, some studies conducted with animal models with an exogenous administration of TGF-β - similar to that of PRP - for the treatment of osteoarthritis have proved that it could have a protective role in vivo, reducing cartilage damage. The role of factors and cytokines usually included in PRP may vary according to the specific pathologies, but for many conditions, reports lack information about their specific effects [14-16].
Due to the variety of production methods, composition and administration routes, PRP is not a standardised product, nor has a unique classification of PRPs been created. One of the most recent proposals, from the Scientific and Standardisation Committee of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis, considers platelet concentrations, preparation method, presence of leukocytes and/or red blood cells and platelet activation method in PRP formulations. However, no definitive classification has been adopted as a reference by researchers or clinicians, and although there have been continuous attempts to optimise PRP production, no consensus has been reached regarding specific standard protocols [17-20].
Despite this lack of standardisation, PRP can be considered an advantageous product because of its wide and effective fields of application, the numerous commercial devices that allow its easy production and its limited adverse events (AEs), considering that it is often used as an autologous derivative. Indeed, the use of PRP seems to be quite safe, with limited AEs reported in a few case reports. The most commonly reported AEs are cases of post-operative infections after a local administration of PRP. However, the cases are limited, and it is still not possible to establish a clear causal relationship between PRP and this kind of AE [21].
The use of allogeneic PRP (e.g., from blood donors) is an emerging topic that could simplify large-scale PRP production and eventual standardisation, with promising effects anticipated in the field of wound healing in the coming years. However, it is still under investigation [22].
Additionally, PRP has proven to be an interesting mediator of not only cell proliferation and angiogenesis but also specific effects on the innate and adaptive immune systems, anti-ageing properties and analgesic effects - topics currently undergoing in-depth analysis for their broader implications. Another interesting and emerging aspect is the possible role that PRP could play in repairing musculoskeletal injuries in combination with rehabilitation techniques, which is addressed in the following sections of this review [12].
The aim of this review is to summarise the most relevant evidence regarding the use of PRP in the treatment of athletes, a specific population more at risk of damage to the musculoskeletal system due to their physical activities. Currently, while many papers focus on the use of PRP for musculoskeletal injuries, only a few explicitly consider athletes as their target, even though they represent a population that could greatly benefit from the regenerative and anti-inflammatory properties of PRP.
PRP acquires a significant role in the treatment of athletic injuries, especially because it can help avoid surgery and shorten the recovery time, thereby increasing the healing response. Although some studies have underlined the limited effect of PRP on certain types of lesions, such as acute muscle injuries, its use is still debated and shows some positive results in different fields, such as tendon and cartilage lesions, which have relevant implications in athletes’ lives [23-25].
Material and methods
our initial search focused on the main musculoskeletal pathologies or injuries affecting athletes and their potential treatment using PRP. The search yielded a total of 2,009 articles on PubMed using the following keywords:
(platelet-rich plasma) AND (athletes) AND (ageing) AND musculoskeletal OR (tendon) AND (contact sport) OR (non-contact sport) AND (professional) OR (amateur) AND (injuries).
(platelet-rich plasma) AND (athletes) AND (injuries) AND (pathophysiology).
(platelet-rich plasma) AND (athletes) AND (injuries) AND (injury) AND (musculoskeletal).
Then, we first selected the articles by applying specific filters on PubMed: we excluded review articles, and only full-text papers were included. We also filtered the articles to include only those referring to humans, with a publication date ranging from 1st January 2014 to 31st July 2024 (this time frame was chosen in advance to select data from the last decade regarding PRP applications on athletes’ injuries). Only papers available in English were considered. Finally, we manually retrieved eligible references, focusing on the main subject of the review. This process has been summarised in our PRISMA flowchart (Figure 1).
Figure 1
PRISMA flow chart. The diagram illustrates the systematic process followed to include papers identified through our search
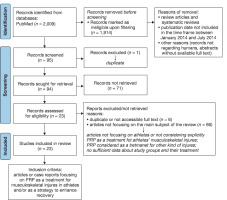
The studies included in this review were categorised based on the anatomical sites and the pathologies described by each reference.
Athletes’ musculoskeletal pathologies and PRP treatment
The following sections focus on musculoskeletal pathologies or injuries that are frequent in athletes, how PRP could be used to treat them and the effectiveness of this treatment. The sections are divided considering the different anatomical segments involved.
Pathologies or injuries of the lower limb
Hamstring injuries are among the most common soft tissue injuries in athletes, particularly in sports that involve sprinting, jumping or sudden changes in direction. These injuries can range from mild strains to severe tears, with recovery times varying from weeks to months. Despite advances in rehabilitation protocols, hamstring injuries are notorious for their high recurrence rates, which can exceed 30% [26].
In the context of hamstring strains, growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), TGF-β, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and insulin-like growth factor-1 are of paramount importance as healing and rebuilding compounds. Therefore, the use of autologous PRP is critical in promoting angiogenesis, collagen synthesis and the recruitment of cells necessary for tissue repair, such as fibroblasts and myoblasts [27]. In 2014, Hamid et al. [28] conducted a study in which a single autologous PRP injection com bined with a rehabilitation program was significantly more effective in treating hamstring injuries than a rehabilitation program alone. Twenty-eight patients were randomly allocated to autologous PRP, and half of the patients in the PRP group made a full recovery, returning to sport 10 weeks earlier than the control group and with lower pain severity events. The PRP group revealed a statistically significant time to return to play (KIP) compared to rehabilitation alone, which led to a later recovery. Hamid et al. [28] demonstrated in their study that at least 50% of the patients in the PRP group achieved a full recovery at week 26, with a mean time to RTP of 26.7 ± 7.0 days, against a full recovery of at least 50% of the patients in the control group at week 39 and 42.5 ± 20.6 days to RTP, and a significant difference in survival function between the two groups, according to the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test (p = 0.006). Furthermore, a Cox regression analysis was used to evaluate several variables, such as age, duration of injury, length of the injured area, active knee range of movement deficit and previous hamstring injury, as covariates to evaluate how these variables could modify the outcome. It was highlighted that only the PRP group demonstrated statistical significance (G2(1) = 5.688, p = 0.017). Finally, only patients treated with PRP had a significant reduction in pain at all time points (p = 0.007). However, subsequent studies did not find the same positive results.
High-ankle sprains or injuries to the ankle syndesmosis can be a fundamental problem in delaying athletes’ return to competition [29]. Laver et al. studied 16 athletes with high ankle sprains, evaluating the RTP time and the reduction of residual pain after two injections of PRGF - a type of PRP enriched with growth factors - administered at the onset and 7 days later. The study was a randomised controlled trial where patients were divided into a treatment group receiving PRGF injections and a control group. The treatment group was characterised by a significantly shorter RTP time and less residual pain compared to the control group [30]. In 2015, Samra et al. [31] conducted a cohort-controlled pilot study involving two groups of rugby players affected by ankle syndesmosis injury: 10 players receiving PRP treatment and 11 control players. The study group was treated with a single ultrasound-guided PRP injection into the anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament. The results showed that this experimental group returned to play significantly faster, with a mean difference in RTP time of 20.7 days less for the intervention group compared with the control group. Moreover, a clear improvement was also observed in other functional outcomes
However, Hamilton et al. [32] found that PRP had a trivial and non-significant effect on RTP time and re-injury risk in professional athletes after hamstring injuries compared to placebo or rehabilitation. Also, Reurink et al. [33] demonstrated that there were no real benefits for intramuscular PRP injections in patients with acute hamstring injuries. The possible reason behind these negative results might be the accuracy of the injection technique, which in Hamilton et al. [32] study was not performed with ultrasonographic guidance, while Reurink et al. [33] used PPP as a placebo instead of saline solution.
In 2022, Trunz et al. [34] evaluated a positive effect of PRP, with a significant reduction in recovery time, by adding intramuscular hematoma aspiration to the treatment. This potentially sped up recovery time compared to previous studies.
Achilles tendinopathy and patellar tendinopathy
Tendinopathy refers to a range of tendon disorders characterised by pain, swelling and impaired function. Achilles tendinopathy and patellar tendinopathy are two of the most prevalent forms, each affecting different tendons with distinct biomechanical and anatomical considerations. Achilles tendinopathy primarily affects the Achilles tendon, the largest and strongest tendon in the human body, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. Typically, it results from repetitive overloading of the Achilles tendon, leading to a cycle of microtrauma and failed healing. The condition is characterised by degenerative changes within the tendon, including collagen disorganisation, increased proteoglycan content and the presence of neovascularisation [35]. Unlike acute tendinitis, which involves inflammation, tendinopathy is primarily a degenerative condition.
Patellar tendinopathy, often referred to as “jumper’s knee”, is similarly caused by repetitive stress, particularly from activities involving high forces through the knee extensor mechanism, such as jumping and landing. The pathology of patellar tendinopathy mirrors that of Achilles tendinopathy, with tendon degeneration, collagen disarray and neovascularisation being key features. However, the patellar tendon is subjected to different mechanical forces compared to the Achilles tendon, which may influence the development and progression of tendinopathy. The condition is often localised at the inferior pole of the patella, where the tendon experiences the highest stress. Both conditions are common in sports that involve repetitive loading, such as running, jumping and cutting movements [36].
The management of Achilles and patellar tendinopathy uses both conservative and innovative measures to stimulate healing processes and reduce pain. Among the innovative measures are PRP injections. Filardo et al. [37], in 2014, treated 27 patients with three ultrasound-guided intra-tendinous injections of PRP at two-week intervals for refractory Achilles tendinopathy. The study concluded that PRP injections provided good results for chronic Achilles tendinopathy with stable outcomes over the mid-term follow-up. In the same year, Charousset et al. [38] evaluated 28 athletes using ultrasound-guided PRP injections for the treatment of chronic patellar tendinopathy. The athletes were treated with three injections once a week, after which 75% of them returned to a pre-pathology sports level, achieving an improvement in their symptoms. In a double-blind, randomised trial, Dragoo et al. [39] analysed the results of treatment with a single ultrasound-guided injection of leukocyte-rich PRP (LR-PRP) on 23 athletes affected by patellar tendinopathy. After 12 weeks, the treated group showed a clear improvement compared to the control group; however, after 26 weeks, the difference was no longer significant. Crescibene et al. [40] used PRP on 14 athletic patients affected by Achilles tendinopathy and seven patients affected by patellar ten-dinopathy with a two-year follow-up, finding a clear decrease in painful symptoms and an enhanced Victorian Institute of Sport Assessment (VISA) score after a 24-month follow-up, equal to 84.2 points on a scale from 0 to 100 (Table 2). Crescibene’s study has profound limitations, including a small number of patients and the lack of a control group. Guelfi et al. [41] treated 46 athletes with mid-portion chronic recalcitrant Achilles tendinopathies with a single administration of PRP, achieving a significant improvement.
Table 2
Victorian Institute of Sport Assessment (VISA) questionnaires
[i] The VISA questionnaires have been developed for the study of lower limb tendinopathies. The table presents distinct types of self-administered VISA questionnaires that focus on different tendinopathies, some of which are covered in this review. The questionnaires assess factors such as pain and functional limitations, with a total achievable score ranging from 0 to 100 (the latter representing the absence of pain or functional impairment).
[ii] VISA-A - A self-report clinical outcome measure used in patients with Achilles tendinopathy. It consists of eight questions that measure the domains of pain, function in daily living and sports activities. It has been found to be a reliable and valid tool for assessing the severity of Achilles tendinopathy. The reliability of the questionnaire has been tested using test-retest reliability, which has been found to be high [46]. VISA-P - A self-report clinical outcome measure used in patients with patellar tendinopathy. It consists of eight questions that measure the domains of pain, function in daily living and sports activities. The psychometric properties of the questionnaire have been evaluated in various studies. The validity and reliability of the questionnaire have been determined in different languages and cultures. However, a recent reliability generalisation meta-analysis claims that greater evaluation with more scientific evidence is required before it can be implemented in clinical practice [47]. VISA-G - A self-report clinical outcome measure used in patients with greater trochanteric pain syndrome (GTPS). It consists of eight questions that measure the domains of pain, function in daily living and sports activities. It is a patient-reported outcome measure tool specifically designed to measure the severity of disability associated with GTPS. However, a recent systematic review evaluating the content and structural validity evidence of the VISA questionnaires showed very low-quality evidence for their content and structural validity [48]. VISA-H - A self-report clinical outcome measure used in patients with proximal hamstring tendinopathy. It consists of eight questions that measure the domains of pain, function in daily living and sports activities. It has high psychometric properties, including validity, reliability and responsiveness. The validity of the VISA-H questionnaire was established through the use of a cross-sectional study design [40].
However, in contrast with these results, Scott et al. [42], in 2019, studied PRP in patellar tendinopathy, verifying the differences between PRP rich in leukocytes and PRP poor in leukocytes compared to a saline solution in a parallel randomised single-blind saline-controlled study. In this study, 61 athletic patients were allocated into three groups, which received a single ultrasound-guided injection of LR-PRP, leukocyte-poor PRP (LP-PRP) or saline placebo. After randomisation, none of the analysed groups showed a significant difference (p = 0.059).
In 2020, Abate et al. [43] studied the factors associated with positive outcomes related to PRP treatment for Achilles tendinopathy, evaluating 84 athletes using the VISA score and ultrasound. It was found that younger age, male sex and good adherence to eccentric training can be considered predictors of better results after PRP therapy. Finally, we wish to highlight the experience of Rodas et al. [44, 45], who tested the use of PRP and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in 20 athletes affected by chronic patellar tendinopathy, concluding that both treatments are effective in reducing pain and aiding recovery from the pathology. Although the results of the stem cell therapy appeared superior to the PRP group, the latter showed potential in treating tendinopathy, especially for patients who failed conservative treatments. However, its efficacy compared to traditional methods remains debated: the decision to use PRP should be tailored to individual patients, case by case, considering factors such as symptom duration and severity [44, 45].
Plantar fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is primarily a degenerative condition, rather than purely inflammatory, which challenges the traditional view of it as plantar “fasciitis”. The term “fasciosis” is often used to describe the chronic phase of the condition, when the degeneration of the collagen fibres within the plantar fascia occurs due to repetitive microtrauma. These degenerative changes are marked by disorganisation of the collagen structure, increased proteoglycan content and an absence of inflammatory cells. The plantar fascia experiences significant tensile stress during activities such as walking, running and jumping. Factors such as high body weight, tight calf muscles, flat feet (pes planus) or high arches (pes cavus) can increase this stress, leading to microtears in the fascia [50]. over time, the body’s healing response may be inadequate, resulting in chronic pain and structural changes in the fascia.
Although there are several studies regarding plantar fasciitis and PRP treatment, only a few studies report data on athletes. Martinelli, in 2012, used five athletes undergoing a three-injection series of PRP treatment for musculoskeletal injuries [51]. Four athletes successfully returned to their sport at the same competitive level within three months. However, one athlete, despite completing the treatment, was only able to return at a reduced level of performance. In a 2013 retrospective review, O’Malley et al. examined the outcomes of 23 patients treated with PRP, finding an improvement in sports and recreational activity levels as measured by the Foot and Ankle outcome Survey [52]. However, this improvement was not statistically significant. In contrast, a 2014 case series by Wilson et al. [53], involving 22 patients, reported both statistically and clinically significant improvements in the Foot and Ankle Ability Measure-Sports Subscale at 32 weeks post-injection, suggesting a more robust benefit from PRP in enhancing foot and ankle function. Other studies in 2016 demonstrated the efficacy of PRP, similar to low-dose radiation treatment, suggesting that it could be more effective than corticosteroids in the long term, although more research is needed [54-56]. In 2023, Alessio-Mazzola et al. [57] compared, in a retrospective study, ultrasound-guided PRP and focal ultrasound-guided extracorporeal shockwave therapy in 55 athletes. The results showed that both practices are valid solutions, although, after treatment with PRP injections, a quicker and more frequent return to sporting activities was recorded in sports practitioners.
The paucity of studies focusing on athletes treated with PRP for plantar fasciitis makes drawing conclusions and recommendations for this population difficult. There are also no randomised controlled trials that report the athletic status of participants.
Pathologies or injuries of the upper limb
Upper limb injuries are prevalent across various populations, particularly among athletes, manual labourers and individuals engaged in activities that require repetitive or high-intensity upper body movements. The upper limb - comprising the shoulder, arm, elbow, forearm, wrist and hand - is essential for a wide range of daily activities and specialised functions [58]. Due to its complex anatomy and the demands placed on it, the upper limb is susceptible to various injuries. These injuries can significantly affect an individual’s ability to perform both routine and occupational tasks, leading to pain, loss of function and a reduced quality of life. Upper limb injuries can be broadly categorised into acute injuries, such as fractures, dislocations and tendon ruptures, and chronic or overuse injuries, such as tendinopathies, bursitis and nerve entrapment syndromes [59].
In 2015, Hoffman et al. [60] explored the possibility of using a dermal allograft, combined with PRP and mesenchymal stem cells, for the reconstruction of an ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) in a professional basketball player to improve healing and accelerate RTP. This case report demonstrated significant improvements in pain and limb function, with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) confirmation of ligament integrity at 3 months and 17 months post-surgery [60]. Dines et al. [61], in 2016, successfully treated 44 high-level throwing athletes who had suffered a partial UCL tear: 16 patients received one PRP injection, 6 patients two injections and 22 patients three injections. Of the 44 patients, 15 (34%) had an excellent result, 17 had a good result, 2 had an average result, and 10 had a poor result. The average time from injection to return to sports was five weeks, and the average time to return to competition was 12 weeks. According to the authors, the use of PRP produced better results than conservative treatments for this type of injury [61].
In 2018, Gordon et al. [62] used PRP to treat a partial tear of the UCL in a 14-year-old teenager. An ultrasound-guided injection, along with standard rehabilitation, allowed the young athlete to make a full recovery and RTP. However, despite this encouraging data, later in 2019, Chauhan et al. [63] published a comparative and matched cohort analysis of544 professional baseball players, of which 133 received PRP, and 411 did not for the treatment of UCL injuries. Although the type of PRP preparation differed in many subjects, potentially introducing an important bias, the study found that players who received PRP had a significantly longer delay in RTP, and PRP did not improve outcomes [63].
The studies reviewed in the literature do not typically report complications following the use of PRP. However, Thompson et al. [64], in 2021, published a case series on three patients - all high-level baseball players - treated with PRP injections for partial UCL injuries. These patients developed cubital tunnel syndrome with significant fibrosis around the ulnar nerve after PRP treatment, requiring surgical intervention to release the cubital tunnel. This indicates that fibrosis could be a potential complication of the use of PRP at this anatomical site. The reason behind the possible fibrosis, in the specific pathological condition raised by Thompson and colleagues, may be related to the action of TGF-β at the specific site of PRP injection. TGF-β influences extracellular matrix (ECM) protein deposition but, at the same time, inhibits enzymes that break down the ECM (such as matrix metalloproteinases) and upregulates tissue inhibitors of these enzymes, contributing to excessive ECM around the ulnar nerve. The modification of the ECM, with a different regulation of the factors that induce the deposition of matrix proteins, could evolve over time into increased fibrosis or a modification of the ratio between type I and type III collagen.
Focusing on lateral epicondylitis, a paper by Xu et al. [65] shows that treating lateral epicondylitis with PRP injection produces long-term pain reduction compared to corticosteroid injection, which is more effective in the short term. In conclusion, although the results of treating tendinopathies with PRP are not as promising, clinical evidence suggests that local injection of PRP may benefit patients with chronic elbow epicondylitis that is refractory to standard non-surgical treatment.
Muscle injuries
Muscle injuries are common in sports and physical activities, accounting for a significant proportion of time lost from competition and training. These injuries can be classified into strains, contusions and lacerations, with strains being the most prevalent. The healing process for muscle injuries involves inflammation, regeneration and remodelling phases, each of which can be lengthy and complex, potentially leading to incomplete recovery or re-injury [66].
Hamilton et al. [32], in 2015, used PRP, PPP or no injection in a randomised, three-arm (double-blind for the injection arms), parallel-group trial of 90 professional athletes with MRI-positive hamstring injuries. The results showed that a single PRP injection, together with an intensive rehabilitation programme, did not reduce the RTP when compared with rehabilitation alone. On the contrary, a single PRP injection in combination with intensive rehabilitation reduced the time to return to sport when compared with a single PPP injection and rehabilitation [34].
Pogliacomi et al. [67], in 2019, published a case report on the use of PRP in the treatment of a rectus femoris myotendinous lesion, using three injections at 10, 20 and 30 days after the injury in a non-professional athlete. The authors described the progressive resolution of the lesion and a return to sports after 90 days. Among other relevant experiences in PRP treatment for muscle injuries, we wish to underline the case report of Lutz and colleagues, who, in 2023, treated a quadriceps tendon tear in a collegiate basketball player using a PRP injection combined with a rehabilitation protocol [68].
Lately, in 2024, de Aysa et al. [69] published a case report of an 18-year-old male professional football player with an acute-on-chronic lateral muscle tear of the distal rectus femoris. He received a 1-ml liquid LR-PRP injection using intermittent ultrasound guidance after seroma aspiration, 34 days after the initial injury. The athlete returned to play 52 days after the injury with no pain, and after one year of follow-up, the patient remained playing at a competitive level, asymptomatic, with no reported re-injury [69].
The use of PRP in muscle injuries has been explored in both experimental studies and clinical settings, with mixed results. Potential benefits of PRP therapy include faster recovery times, reduced pain and a lower risk of re-injury. However, the efficacy of PRP can vary depending on factors such as the type of injury, the PRP preparation, the timing of administration and the rehabilitation protocol [70]. Although there is evidence supporting the potential use of PRP in athletes, further studies are needed to fully establish its efficacy in repairing muscle injuries.
Conclusions
Injection therapies, such as PRP, present an effective and safe option for athletes’ rehabilitation. The major appeal lies in its potential to minimise time lost from training and competitive play, which aligns well with the goals of conservative management approaches in musculoskeletal rehabilitation. PRP has emerged as a viable non-operative treatment for knee osteoarthritis, though current evidence supporting its standard use in professional athletes remains limited.
Although PRP is a valuable intervention for enhancing healing and recovery times, a critical consideration is its potential to improve athletic performance, which may bring it under the scope of anti-doping regulations. PRP has long been the subject of debate in the scientific community in this regard, and to date, the most widely recognised regulatory body, the World AntiDoping Agency (WADA), has thoroughly analysed the issue, ultimately arriving at the following conclusion: orthobiological therapy using PRP is currently used as a long-term regenerative treatment aimed at healing worn or traumatised tissues. To date, there is no evidence that clearly points towards a consistent or immediate increase in sports performance following PRP use. Furthermore, PRP is injected directly into the tissue or joint affected by trauma, where it acts locally without any evident systemic effect, assisting only with local healing. For these reasons, PRP is not currently included among the methods considered as doping; therefore, it can be used by athletes, regardless of the sport they practise, but with the indications and applications mentioned above. However, both in the 2024 version and in the version that will come into force on 1st January 2025, WADA maintains in its “World Anti-Doping Code International Standard Prohibited List” - the list of all molecules, compounds or treatment methods prohibited before, during and after athletic competitions - some of which are certainly present in PRP. Among these are PDGF, fibroblast growth factors and VEGF. Therefore, it is possible that in the future, WADA’s position may change, depending on the updating of clinical and scientific knowledge regarding the functioning of PRP.
In conclusion, while PRP therapy holds promise, several practical challenges remain. The preparation of PRP lacks standardisation, with variations in platelet concentration, activation methods and the use of leukocyte-rich or leukocyte-poor preparations [71]. These differences can affect the therapeutic efficacy of PRP, making it difficult to compare results across studies or establish consistent treatment protocols. The timing of the injection is another critical factor. Some evidence suggests that early administration of PRP, within the first few days following an injury, may be more beneficial in promoting muscle regeneration. However, the optimal timing for PRP application remains under investigation, and further research is needed to establish clear guidelines [72]. Additionally, the cost of PRP therapy can be a barrier to its widespread use, particularly because insurance coverage for PRP in musculoskeletal injuries is limited in many regions. Furthermore, the lack of standardisation also has cost implications. Tailoring PRP preparations to individual needs without standard protocols can lead to inefficiencies, increasing treatment costs without guaranteeing improved outcomes. Moreover, given the lack of consensus, it is not possible to accurately estimate the actual cost of treatment because each commercial kit has its own price, and there are no definitive data to determine which product might provide the best results [73,74]. Establishing well-defined protocols could help reduce costs by optimising dosing, administration frequency and duration of therapy, thereby maximising benefits while avoiding overuse. Standardised guidelines would not only improve the reproducibility of research but also enable clinicians to make evidence-based decisions, enhancing PRP’s value as a cost-effective treatment option. High-quality clinical trials are essential to determine optimal formulations, dosages and administration techniques, particularly in sports settings where quick recovery and minimal downtime are priorities. This approach would enable healthcare providers to deliver effective, economically feasible PRP therapies, offering a practical, ethical and financially responsible option for athlete rehabilitation and joint preservation.


