Introduction
Dyslipidaemia is a multifaceted lipid metabolic disorder that results in alterations in blood lipids, leading to cardiovascular disease (CVD) - the most common cause of death globally [1]. Dyslipidaemia is a condition defined by elevated levels of LDL cholesterol (LDL), total cholesterol (TC), and triglycerides (TG), alongside decreased levels of HDL cholesterol (HDL) [2, 3]. These alterations have the potential to damage the arterial endothelium, initiating atherosclerosis and increasing the risk of various diseases such as stroke, myocardial infarction, and peripheral vascular disease [4, 5]. Elevated levels of LDL and serum total cholesterol have been associated with an increased risk of mortality from CVD, which remains the leading cause of death worldwide, accounting for approximately 32% of all fatalities in 2019 [6].
Regular physical exercise has been suggested as a non-pharmacological treatment option for dyslipidaemia [7]. It has been shown to be an effective, safe, and inexpensive strategy. Previous research has demonstrated that HDL levels increase within 24 hours following aerobic exercise sessions [8]. Additionally, regular exercise boosts HDL levels in a dose-response manner and is associated with reduced cardiovascular morbidity and mortality [9, 10]. For example, Tai Chi, a Chinese exercise that combines deep breathing and meditation, has been shown to lower blood TG levels and help prevent hypertension in middle-aged and elderly. individuals [11-13]. Similarly, Qigong, another traditional Chinese activity, significantly reduces TG and LDL levels when compared to no exercise [14].
Ruesi Dadton (RSD) is a Thai mind-body exercise that incorporates slow body movements with deep breathing, similar to yoga and Tai Chi. It is performed as part of a multimodal exercise program [15]. Previous studies have indicated that RSD improves both cognitive and movement abilities in patients with mild cognitive impairment, reduces oxidative stress, and enhances quality of life [16]. However, the impact of RSD exercise on blood lipid profiles in overweight individuals has not been comprehensively investigated. Thus, the objective of this study was to compare the effects of RSD on lipid profiles, such as TG, TC, LDL, and HDL, physical performance, and anthropometric indices such as BMI, waist circumference (WC), waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) and waist-to-height ratio (WHtR) against standard lifestyle guidelines that are not pharmacologically managed.
Material and methods
Study design
The study was conducted as a single-blinded randomised controlled trial, with the investigator blinded to the participant assignments. It took place at the outpatient Department of the Thai Traditional and Alternative Medicine Hospital in Bangkok, Thailand.
Participants and sample size
The sample size for the study was calculated using the G*Power program with a medium effect size d of 0.5, 80% power, and a significance level of 0.05. Initially, 58 participants were required; however, to account for potential dropouts, this number was increased by 10% to 64 participants. Inclusion criteria included being aged 18-70 years, having a BMI between 25 and 29.90 kg/m2, and having total cholesterol levels over 200 mg/dL. Exclusion criteria included participation in other research projects; a diagnosis of dyslipidaemia; current use of statins or other lipid-modifying treatments; the presence of severe comorbid conditions such as advanced heart disease, uncontrolled hypertension, liver or renal disease, or uncontrolled diabetes, that could interfere with study outcomes; and the use of herbal medicines or other non-pharmaceutical cholesterol-lowering agents.
Intervention
Eligible participants were enrolled in the study after screening, and baseline characteristics were documented. Before starting the intervention, both groups received education on lifestyle modifications for managing body weight and cholesterol levels from healthcare providers. Participants in the RSD group were taught breathing techniques during two on-site sessions, each lasting 60 minutes, at the Thai Traditional and Alternative Medicine Hospital in Bangkok, Thailand. This was followed by a 12-week online intervention supervised by a Thai Traditional Medicine (TTM) practitioner. During this period, participants were required to perform 60 minutes of RSD exercise three times a week, for a total of 36 sessions. Videos were recorded and sent to the TTM coach at the end of each session for review. The RSD protocol consisted of slow stretching combined with deep breathing exercises, including a 10-second breath hold followed by a gentle exhale. The exercise regimen included a 5-minute warm-up to relax and prepare the joints and muscles, a 50-minute main exercise phase aimed at enhancing muscle strength and balance, and a 5-minute cooldown period, as shown in Table 1. The control group received a standard self-care manual, which included guidelines on maintaining a healthy diet, limiting dietary lipid intake, and engaging in regular physical exercise three times per week for at least 60 minutes, but they did not engage in the mind-body exercises practised by the intervention group until after the study period.
Table 1
The exercise intervention program
Data collection
Physical and laboratory examinations were meticulously conducted by professional testing personnel to gather comprehensive data on the participant’s weight, height, and blood lipid levels. To ensure the highest accuracy, participants were instructed to fast for 8 hours prior to undergoing blood tests in the morning. The lipid profile was assessed using an enzymatic colouri-metric method with a high-sensitivity analyser, which is renowned for its precise detection capabilities and suitability for clinical studies.
Plasma lipid profiles were determined at baseline and week 12 using specific reagent kits from Abbott Laboratory. LDL concentrations were measured using the Alinity c Direct LDL Reagent Kit 07P71, which has a coefficient of variation (% CV) of less than 1.5%. HDL levels were quantified using the Alinity c Ultra HDL Reagent Kit 07P75, with a % CV of less than 2.2%. Triglycerides were assessed using the Triglyceride Reagent Kit 04U06, with a % CV of less than 1.8%. The obtained % CV values were benchmarked against standard reference values, ensuring compliance with accepted standards. These measurements were carried out using the Alinity c autoanalyser (Abbott Laboratories, Chicago, IL, USA). The reference ranges employed were as follows: TC: 125-200 mg/dL; HDL: > 40 mg/dL for males, > 50 mg/dL for females; LDL: < 130 mg/dL; and TG: < 150 mg/dL [17].
Anthropometric assessments were measured at baseline, week 4, week 8, and week 12, the measurements included the triceps skinfold (TSF), WC, WHR, and WHtR. These were meticulously recorded by well-trained health technologists and recorders, adhering to standardised examination protocols. Physical performance was evaluated using the Time Up and Go Test (TUGT) and Chair Sit-and-Reach Test (CSRT), both recognised as valid and reliable methods for assessing mobility and flexibility, respectively [18-21]. Additionally, the SF-12 Health Survey (standard) was used to assess the quality of life of participants [22, 23], providing insights into the subjective perception of health and well-being associated with changes in physical activity and lipid profiles, which were assessed at baseline and the end of the study (week 12).
Data analysis
IBM SPSS version 24 was used for statistical analysis. A significance level (alpha) of 0.05 was set to determine statistical significance. The normality of all outcome variables was assessed using the Shapiro-Wilk and Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests. Descriptive statistics, including frequency, percentage, mean, and standard deviation, were calculated for both the RSD and control groups. For lipid profiles and quality of life measures, paired sample f-tests were used to evaluate within-group differences between baseline and week 12, while independent f-tests were used to assess between-group differences at baseline and week 12. For physical performance and anthropometric indices, a two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with repeated measures was employed to examine the main effects of time (baseline, week 4, week 8, and week 12) and group (RSD vs. control) on the outcome variables.
Results
Baseline characteristics
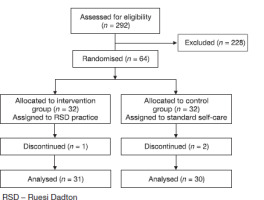
In this study, 292 participants were assessed for eligibility, 64 met the inclusion criteria and were enrolled and randomised into two groups. At the end of the study, 61 participants remained: one from the RSD group withdrew early due to a family condition, and two from the control group relocated and withdrew from the study, as depicted in Figure 1. The final analysis included 61 participants (RSD group, n = 31; control group, n = 30). There were no significant differences between the groups in terms of age, marital status, education, occupation, income, vital signs, BMI, WC, underlying diseases, smoking and drinking status, or lipid profiles (TC, TG, HDL, and LDL), as shown in Table 2.
Table 2
Characteristics of the participants at the baseline
Lipid profiles
In this study, we investigated how RSD exercise affected lipid profile regulation. The findings indicated that TC levels showed a decreasing trend in the RSD group from 203.68 ± 36.23 mg/dL at baseline to 193.52 ± 30.89 mg/dL at week 12, while the control group showed a significant increase from 197.56 ± 28.5 mg/dL to 213.04 ± 36.13 mg/dL (p < 0.05). Between-group comparison at week 12 showed significantly lower TC levels in the RSD group (p < 0.05). For LDL levels, the RSD group showed a significant reduction from 141.52 ± 32.29 mg/dL to 125.68 ± 26.74 mg/dL (p < 0.05), while the control group’s LDL significantly increased (p < 0.05). The between-group comparison at week 12 also showed a significant difference favouring the RSD group (p < 0.05). TG levels remained stable in the RSD group, with no significant change, while the control group showed a non-significant upward trend. No significant between-group differences were observed in TG levels at week 12. Additionally, HDL levels showed no significant changes within or between groups, as shown in Table 3.
Table 3
The lipid profiles
Physical performance and anthropometric indices
Physical performance was evaluated using the TUGT and CSRT. Both tests demonstrated significant improvements in agility and physical flexibility after the experiment (p < 0.05), as presented in Table 4. However, the interaction effect between group and time variables for TUGT and CSRT was not statistically significant, with F-values of 0.28 and 0.14, respectively
Table 4
The values of physical performances and anthropometric indices
Anthropometric indicators, including TSF, WC, WHR, and WHtR, were also assessed. Post-intervention, the RSD group exhibited significant reductions in TSF, WC, and WHR, whereas the control group showed increasing trends in these parameters (Table 4). Despite these trends, the interaction effects between group and time variables for TSF, WC, WHR, and WHtR were not statistically significant, with F-values of 0.42, 0.29, 0.48, and 1.22, respectively.
Quality of life
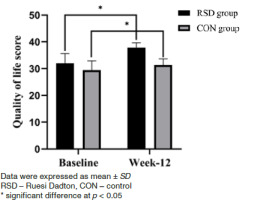
In terms of quality of life, both groups showed significant improvements following the intervention (p < 0.05). Specifically, the RSD group exhibited an increase in the mean ± standard deviation of their quality-of-life score from 31.96 ± 3.68 at baseline to 37.8 ± 1.89 by the end of the study. Similarly, the control group also experienced an increase, with their scores rising from 29.44 ± 3.44 to 31.36 ± 2.27. However, no significant differences were observed between the groups, as shown in Figure 2.
Discussion
RSD, similar to yoga, Tai Chi and Qigong, is a form of mind-body exercise that combines physical movement with mental focus and controlled breathing [16]. These physical activities are recommended as lifestyle interventions to enhance physical performance and health [24, 25]. The results of our study indicate that RSD exercise has a positive effect on lipid profiles and physical performance in overweight Thai individuals. These findings align with previous research that highlights the benefits of mind-body exercises on lipid metabolism and overall health [26]. Several studies have suggested that these exercises help control dyslipidaemia [27, 28]. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first trial to examine the effects of RSD, a Thai exercise, on lipid profiles and physical functions in overweight Thai individuals. After 12 weeks, participants in the RSD group showed significantly lower levels of TC and LDL compared to the control group. However, no differences were observed in HDL and TG levels.
RSD also had beneficial effects on TSF, WC, and WHR in overweight individuals compared to the control group. Exercise has been shown to reduce cholesterol levels and improve the pathophysiology and physical fitness of individuals with dyslipidaemia [29, 30]. It is also a popular strategy for treating obesity and reducing the risk of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) [31, 32]. Multiple systematic reviews and meta-analysis have demonstrated that exercise significantly improves serum lipid levels in people with hyperlipidaemia by increasing HDL levels and lowering TG, TC, and LDL levels [33, 34]. According to guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias, it is consistently advisable to recommend regular physical exercise of moderate intensity, comprising a duration of at least 30 minutes per day, to individuals with dyslipidaemia, regardless of weight [35]. However, adherence to these guidelines is typically low among middle-aged and older individuals, often due to reduced cardiopulmonary function and joint discomfort [36]. As a result, gentle and slow exercises are deemed suitable for middle-aged and older adults.
Numerous studies indicate that mind-body exercises, such as Tai Chi and Baduanjin, are becoming increasingly popular among middle-aged and older adults to improve lipid profiles and body shape [37, 38]. In Thailand, RSD is a mind-body exercise that blends slow and gentle movement with controlled deep breathing and mindfulness meditation throughout sessions [15]. We found that LDL levels and TC in the RSD group decreased, whereas they increased in the control group. Conversely, there was no difference in HDL and TG levels.
Our results are supported by a prior study that found Tai Chi training significantly decreases TC levels while having no effect on HDL levels [39]. In addition, Tai Chi also reduces LDL levels [40]. Furthermore, baduanjin exercises, a form of Qigong, significantly decrease plasma TC, TG, and LDL levels while significantly increasing HDL concentrations [41]. Regular practice of yoga, for example, significantly decreases stress and anxiety, which in turn reduces cortisol levels - a hormone linked to higher blood lipid levels [42]. Additionally, yoga enhances the balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, leading to improved lipid metabolism [43, 44], increases metabolic rate and promotes lipid utilisation, resulting in lower levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides and higher levels of HDL cholesterol [43, 45]. Moreover, yoga exhibits anti-inflammatory effects, reducing markers like C-reactive protein and interleukin-6, which are associated with dyslipidaemia [46, 47]. For RSD, it has been found to improve blood pressure and decrease oxidative stress in healthy elderly individuals [48]. In light of these results, RSD exercise should be promoted as an alternative exercise method for middle-aged and elderly patients with dyslipidaemia.
According to the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) guidelines, the primary preventative strategy in low-risk groups is lifestyle guidance and statin medication. Additionally, LDL levels should be maintained below 70 mg/dL [35]. Our investigation found that LDL levels of overweight patients significantly decreased from 141.52 ± 32.29 to 125.68 ± 26.74. Although this was a significant reduction, it did not meet the target level. We hypothesise that RSD exercise has a gradual effect, making it challenging to reverse the disease progression in such patients quickly. This theory is supported by the fact that traditional Chinese exercises like Baduanjin require an intervention period longer than six months to produce noticeable results [49].
For physical performance and anthropometric indices, the RSD group observed a significant decrease in TSF, WC, and WHR (p < 0.05). However, the control group exhibited increases in TSF, WC, WHR, and WHtR. Recent research demonstrated that traditional Chinese exercises, such as Qigong and Baduanjin, can successfully increase muscle strength, balance, and physical performance [50]. Conversely, we discovered the deterioration of blood lipid profiles and anthropometric measurements in the control group. This may be due to the lack of engagement from patients in the control group, who did not provide the researcher with their activity records. As a result, future research may require each patient to document their physical activity.
There are some limitations to this study. Not all observations were statistically significant, possibly due to the small sample size. Thus, further research with larger sample sizes is needed to verify these findings. Additionally, a longer duration may improve the effectiveness of RSD in lowering lipid profiles. Future research should also compare RSD to other physical activities, such as aerobic exercise and strength training, and explore the use of RSD in combination with calorie restriction. Moreover, while the researchers provided participants with a standard self-care manual, which included guidelines on maintaining a healthy diet, limiting dietary lipid intake, and engaging in regular physical exercise, participants’ dietary intake was not directly monitored or recorded through diet logs. This lack of dietary tracking is a limitation, as changes in diet can significantly impact lipid profiles. Future studies should consider incorporating dietary logs to better control for these variables and enhance the accuracy of the results.