Introduction
Education serves as the foundational mechanism for cultivating enduring human virtues [1, 2]. Physical education (PE), sports, and health use focused values-based learning to cultivate the skills needed in the 21st century [3]. More skills are needed in 21st-century learning targeted at enhancing critical and creative thinking abilities [4]. It is through the educational journey that children are inspired to unlock their potential across cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains [5]. Implementing education in the form of a learning process requires special strategies that adapt to student needs [6–8]. One of these involves making adjustments for students with disabilities. Individuals with disabilities possess equal entitlement to education [9]. PE has been taught starting in elementary school [10], illustrating how important PE is to forming a healthy generation [11]. The focus of adapted PE is to cater to the PE needs of all students, particularly those with disabilities [12, 13]. Essentially, children with special needs possess the capacity to engage in learning similar to their developing peers, adjusting their approach to accommodate their unique challenges [9]. PE learning for students with special needs in Indonesia is called adaptive PE.
Adaptive PE serves as a comprehensive learning approach, focusing on nurturing motor skills, physical abilities, social interaction, and individual well-being [14]. Consequently, PE holds significant importance for students with special needs [15], facilitating their physical and mental development and fostering a healthy lifestyle [16]. The distinctive hallmark of incorporating adaptive PE in schools lies in its multifaceted impact on learning outcomes, extending beyond mere adherence to the curriculum. Specifically, educators delineate three primary objectives: academic progress, scholastic attainment, and developmental milestones. Of these, scholastic advancement stands out prominently within this institution’s adaptive PE framework [17]. The pedagogical approach to adaptive PE follows a structured process encompassing assessment, program planning via detailed lesson plans, execution, and thorough evaluations [18]. However, the results of observations in several elementary schools in the West Sumatra region show that no evaluation has ever been carried out, especially on adaptive PE learning. This is an update to this research. In addition, this study only focused on deaf students. Students with hearing impairment have a disability of hearing so it causes a complex problem and affects their speaking ability (oral skills). Students with hearing impairment showed that they have difficulty speaking properly, and they are not familiar with the correct pronunciation of words, sentences, and rhythms [12, 19]. PE learning is necessary and important for deaf students [20]. For deaf students, PE offers additional advantages, notably fostering social inclusion. However, numerous hurdles must be addressed in adapting PE for this demographic, such as the shortage of bilingual teachers and the absence of specific signs for key PE terminology [12]. This is also supported by previous research on adaptive PE learning.
Utilizing the floor time methodology has shown promising results in enhancing the educational achievements of students with cerebral palsy through adaptive PE, particularly in mastering the side roll technique [9]. The floor time method is a learning approach that encourages spontaneous play and conversation. It involves spending at least 20 hours a week engaging with children at their level, often by sitting on the floor to interact and participate in their activities [21]. According to prior research, the assessment of the integration of adaptive PE during the CoVID-19 pandemic in Special Schools in Yogyakarta City yielded outcomes categorized as unsatisfactory [22]. According to these findings, it is evident that the execution of adaptive PE learning at SLB Negeri 1 Dompu during the 2022/2023 academic period has made a beneficial impact on educational inclusivity, as reflected in a student engagement rate of 85% during the learning process [23]. The challenges experienced by students with special needs underscore the difficulty they encounter in adapting to mainstream students in receiving instruction, particularly in PE classes. Hence, evaluation is imperative to facilitate enhancements for future efforts [19, 22, 24]. Creating and assessing tailored e-learning modules for individuals with hearing impairments, utilizing the advanced Adaptation Pedagogical Index methodology. The Adaptation Pedagogical Index methodology consists of three dimensions including learning style, media, and interaction. This method was designed specifically for deaf and hard-of-hearing students so that it suits the characteristics of deaf students [25]. Earlier studies focused on assessing the Learning outcome Evaluation System in Health and PE classes, specifically at the junior high school level [26]. CIPP Evaluation on PE learning in sports and health in special schools in Yogyakarta shown to be good [27]. The overall quality of educational learning in the Special School using CIPP for the South Kalimantan Province is rated as good [28].
Based on previous research, adaptive PE learning requires evaluation in its implementation, and one of the evaluation methods uses CIPP. The CIPP model, an evaluation framework, is divided into four aspects: context, input, process, and product [29, 30]. These aspects can yield comprehensive results in the evaluation process [28]. Evaluation using CIPP in sports learning for deaf students is the right method because it can show all aspects of learning. In the initial study of SLB in West Sumatra, the evaluation process was not yet available for teachers and students. This is because deaf students are difficult to condition, so they need more assistance. However, evaluations can still be carried out on teachers who are directly involved in learning at special schools in West Sumatra.
The novelty of this research is the evaluation of adaptive PE learning using CIPP by teachers for deaf students at special elementary schools. Therefore, this research aims to find out the evaluation of adaptive PE learning using the CIPP method for deaf students in Special Elementary Schools in West Sumatra.
Material and methods
The study described in this article employs an evaluation model approach [10, 31, 32] to assess the efficacy of adaptive PE instruction. Specifically, this research utilizes the CIPP (Context, Input, Process, and Product) model for evaluation. The participants in this study were teachers who taught PE in West Sumatra, Indonesia, with a sample size of 60 teachers selected through purposive sampling. Data collection was carried out through a research instrument in the form of a questionnaire given via Google Forms [33]. The instruments in this research must be tested for validity and reliability [34], which is presented in Appendix 1, an instrument in the form of a questionnaire is declared valid. The results show that all statement items were valid, so reliability testing can be continued. The reliability test is presented in Appendix 2, which shows that all question items are reliable. Participants filled out the Google form according to the instructions given and needed to fill in 59 statement items using Likert scale categories ranging from 1–4 covering aspects of context, input, process, and product for adaptive PE learning [35]. Assessment of adaptive PE learning was performed using the following criteria: very good (76–100%), good (51–75%), enough (26–50%), and poor (1–25%). Descriptive percentages were employed as the data analysis technique in this study.
Results
The results of this research will be presented in the form of a description of sample characteristics and extraordinary elementary schools in West Sumatra, then continued with the results of each CIPP component, and finally the overall average evaluation of adaptive PE learning (Table 1).
Table 1
Sample characteristics
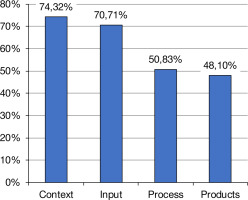
Based on the Table 2, there are 19 regions in West Sumatra with a total of 60 special schools. Next, the results of the CIPP evaluation on PE learning will be presented (Figure 1).
Table 2
Description of special elementary schools in West Sumatra, Indonesia
Based on the research results, the context aspect results obtained 74.32%, the input aspect was 70.71%, the process aspect was 50.83%, and the product aspect was 48.10%. Table 3 presents the average results of the four aspects for evaluating adaptive PE learning below.
Table 3
Results of evaluation adaptive physical education learning
| No. | Aspects | Mean (%) | Results (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Context | 74.32 | |
| 2 | Input | 70.71 | 60.99 |
| 3 | Process | 50.83 | |
| 4 | Products | 48.10 |
The average results for the context, input, process, and product aspects obtained a percentage of 60.99%.
Discussion
According to the findings of the research, the evaluation across various dimensions yielded positive results. Specifically, the context aspect scored 74.32%, indicating a good category, while the input aspect reached 70.71%, indicating a good category. Similarly, the process aspect attained a score of 50.83%, indicating an enough category, and the products aspect achieved 48.10% as an enough category. The average performance across all context, input, process, and product dimensions was 60.99%. The evaluation results using CIPP in adaptive PE learning for deaf students at special elementary schools are in the good category. A parallel study focusing on evaluating the adaptive PE curriculum revealed that the implementation of the Special Elementary Schools’ Penjasorkes curriculum demonstrates proficiency across various aspects. The preliminary assessment of syllabus formulation, lesson plans, teaching materials, and class proficiency reflects commendable performance. Similarly, the review of the transactional process during learning implementation and assessment exhibits effectiveness. However, in evaluating outcomes, particularly in tailoring assessments to accommodate various types of student disabilities, there exist areas requiring improvement [36]. According to the study findings, it can be deduced that the execution of online PE instruction at West Nias Regency Public High School falls within the “less” category [35].
In this research, context aspects rated as good encompass learning materials, learning objectives, organization of materials, media, and additional learning resources, design of teaching and learning activities, classroom management, and evaluation. Regarding the input aspect, the good category includes the suitability of learning materials with educational objectives and learner characteristics. The process aspect falls within the sufficient category, covering learning activities, PE, and participant education activities. The product aspect yielded results in the sufficient category, specifically addressing learning outcomes. Based on the results of this research, the implementation of adaptive physical learning in West Sumatra at the special elementary school level still needs to be improved and enhanced.
Education stands as a cornerstone in the advancement of a nation, as the calibre of education directly influences the quality of its human capital [29]. Hence, the significance of evaluations in education cannot be overstated [37]. This is because evaluation is an integral part of the learning process [31, 37–40]. In this study, the evaluation of context comprised assessments based on indicators of learning philosophy and educational objectives [26]. The second component, referred to as input, encompasses all the plans, strategies, and budget allocations associated with the chosen approach for implementation [41]. Within the process dimension, it is crucial to prioritize adaptable learning methodologies that cater to the diverse needs of students, particularly those with special requirements [33]. In terms of the product aspect, it is imperative to deliver precise information, foster student engagement, increase motivation, enhance institutional efficacy, and elevate the overall standards of education [37].
Conclusions
This research concludes that the evaluation of using CIPP is that the context aspect scored 74.32%, and the input aspect reached 70.71%, indicating good categories. Similarly, the process aspect attained a score of 50.83%, and the products aspect achieved 48.10%, indicating both as enough categories. The average results for the context, input, process, and product aspects obtained a percentage of 60.99%, which shows that the evaluation using CIPP in adaptive PE learning for deaf students at Special Elementary Schools is in the good category. This research is limited only to deaf students, so further research should evaluate students with other special needs and at junior and senior high school levels.